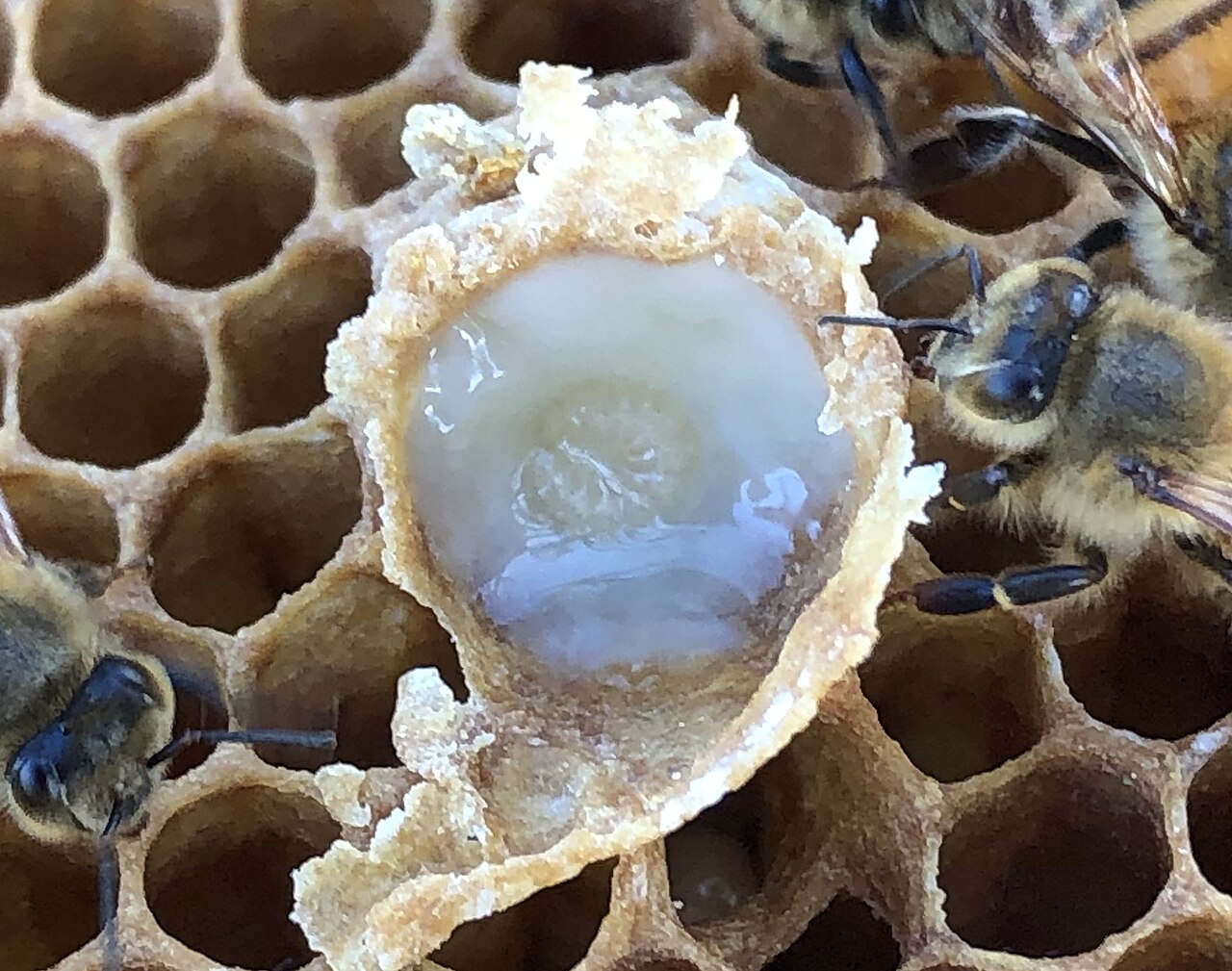
Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is secreted by nurse bees between the ages of 5 and 15 days. During periods of intense egg-laying, not only the queen larvae but also the queen bee herself feeds on royal jelly.
Physical Properties and Chemical Composition of Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is a creamy, opaque, white, or cream-colored substance with a sweet and slightly sour taste and a specific aroma. Lyophilized royal jelly is a highly hygroscopic, white or cream-colored powder that becomes sticky when exposed to moisture.
Studies have shown that royal jelly is a complex and nutrient-rich product, the quality of which depends on the age of the larvae, the physiological state of the bees, the strength of the colony, the collection period, storage conditions, and other factors.
Royal jelly is rich in proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, organic acids, amino acids, and more. It contains 45% proteins, 20% free amino acids, 20% carbohydrates, and 15% fats. Among the mineral substances, royal jelly contains potassium salts, calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, iron, sulfur, gold, silver, and others.
Among the enzymes, it includes amylases, catalase, ascorbic oxidase, and more.
The medicinal properties of royal jelly are also attributed to the presence of radioactive elements in its composition.

Medicinal Uses of Royal Jelly
Royal jelly is used to treat cardiovascular diseases, atherosclerosis, digestive system disorders, bronchial asthma, neurosis, and angina pectoris.
Royal jelly mixed with honey is an excellent remedy for treating stomach and duodenal ulcers.
It helps regulate metabolism, strengthens the body's resistance to infections, stabilizes blood pressure, and enhances memory and vision.
Some experts recommend using royal jelly in combination with honey, propolis, and pollen. However, it is not recommended for individuals allergic to bee products. Various medicinal products are made from royal jelly, including lyophilized powders, tablets, suppositories, and 3% royal jelly ointments.
In Romania, royal jelly is considered a natural food product and even a preventive medicine.
In Bulgaria, food stores offer royal jelly mixed with honey (1 g of royal jelly per 10 g of honey), which is stored at temperatures below 20°C.
Adults can take 10 g of this mixture daily, while children can take 5 g as a tonic and immune-boosting supplement.
Internationally, the following medicinal products derived from royal jelly are available: Apiserum, Apifortil, Lacapis, Royal Jelly, and others.
Royal jelly is also used in the cosmetics industry for the production of various creams. It is also included in some lotions and soaps.
Collection and Storage of Royal Jelly
Among the numerous technological methods for obtaining royal jelly, the highest yield is achieved when the queen bee is isolated. This method, compared to orphaned colonies, does not significantly disrupt the normal life of the bee family or alter its biology.
Royal jelly is collected at the end of spring and the beginning of summer, when there is a large bee population, the brood is capped, and nectar and pollen sources are abundant. Strong colonies with a large number of young bees are preferred.
During the production of royal jelly, specific procedures must be followed to preserve its full biological properties. The apiary must maintain sanitary and hygienic conditions that meet the requirements for medicinal product manufacturing.
Although royal jelly has antimicrobial properties, it is a highly unstable product that rapidly changes not only in appearance but also in properties if stored improperly.
Royal jelly loses its biological properties when exposed to daylight, stored in non-airtight containers, or kept in humid conditions. It can be stored well for six months in a refrigerator at 2-5°C, while at -15°C to -18°C, it can retain its properties for a year.
Lyophilized royal jelly remains well-preserved for years. It is stored in dark, tightly sealed containers.